Wednesday, October 31, 2007
Sunday, October 28, 2007
40 Tips for optimizing your php Code
- If a method can be static, declare it static. Speed improvement is by a factor of 4.
- echo is faster than print.
- Use echo's multiple parameters instead of string concatenation.
- Set the maxvalue for your for-loops before and not in the loop.
- Unset your variables to free memory, especially large arrays.
- Avoid magic like __get, __set, __autoload
- require_once() is expensive
- Use full paths in includes and requires, less time spent on resolving the OS paths.
- If you need to find out the time when the script started executing, $_SERVER[’REQUEST_TIME’] is preferred to time()
- See if you can use strncasecmp, strpbrk and stripos instead of regex
- str_replace is faster than preg_replace, but strtr is faster than str_replace by a factor of 4
- If the function, such as string replacement function, accepts both arrays and single characters as arguments, and if your argument list is not too long, consider writing a few redundant replacement statements, passing one character at a time, instead of one line of code that accepts arrays as search and replace arguments.
- It's better to use select statements than multi if, else if, statements.
- Error suppression with @ is very slow.
- Turn on apache's mod_deflate
- Close your database connections when you're done with them
- $row[’id’] is 7 times faster than $row[id]
- Error messages are expensive
- Do not use functions inside of for loop, such as for ($x=0; $x <>
- Incrementing a local variable in a method is the fastest. Nearly the same as calling a local variable in a function.
- Incrementing a global variable is 2 times slow than a local var.
- Incrementing an object property (eg. $this->prop++) is 3 times slower than a local variable.
- Incrementing an undefined local variable is 9-10 times slower than a pre-initialized one.
- Just declaring a global variable without using it in a function also slows things down (by about the same amount as incrementing a local var). PHP probably does a check to see if the global exists.
- Method invocation appears to be independent of the number of methods defined in the class because I added 10 more methods to the test class (before and after the test method) with no change in performance.
- Methods in derived classes run faster than ones defined in the base class.
- A function call with one parameter and an empty function body takes about the same time as doing 7-8 $localvar++ operations. A similar method call is of course about 15 $localvar++ operations.
- Surrounding your string by ' instead of " will make things interpret a little faster since php looks for variables inside "..." but not inside '...'. Of course you can only do this when you don't need to have variables in the string.
- When echoing strings it's faster to separate them by comma instead of dot. Note: This only works with echo, which is a function that can take several strings as arguments.
- A PHP script will be served at least 2-10 times slower than a static HTML page by Apache. Try to use more static HTML pages and fewer scripts.
- Your PHP scripts are recompiled every time unless the scripts are cached. Install a PHP caching product to typically increase performance by 25-100% by removing compile times.
- Cache as much as possible. Use memcached - memcached is a high-performance memory object caching system intended to speed up dynamic web applications by alleviating database load. OP code caches are useful so that your script does not have to be compiled on every request
- When working with strings and you need to check that the string is either of a certain length you'd understandably would want to use the strlen() function. This function is pretty quick since it's operation does not perform any calculation but merely return the already known length of a string available in the zval structure (internal C struct used to store variables in PHP). However because strlen() is a function it is still somewhat slow because the function call requires several operations such as lowercase & hashtable lookup followed by the execution of said function. In some instance you can improve the speed of your code by using an isset() trick.
Ex.
if (strlen($foo) <> - When incrementing or decrementing the value of the variable $i++ happens to be a tad slower then ++$i. This is something PHP specific and does not apply to other languages, so don't go modifying your C or Java code thinking it'll suddenly become faster, it won't. ++$i happens to be faster in PHP because instead of 4 opcodes used for $i++ you only need 3. Post incrementation actually causes in the creation of a temporary var that is then incremented. While pre-incrementation increases the original value directly. This is one of the optimization that opcode optimized like Zend's PHP optimizer. It is a still a good idea to keep in mind since not all opcode optimizers perform this optimization and there are plenty of ISPs and servers running without an opcode optimizer.
- Not everything has to be OOP, often it is too much overhead, each method and object call consumes a lot of memory.
- Do not implement every data structure as a class, arrays are useful, too
- Don't split methods too much, think, which code you will really re-use
- You can always split the code of a method later, when needed
- Make use of the countless predefined functions
- If you have very time consuming functions in your code, consider writing them as C extensions
- Profile your code. A profiler shows you, which parts of your code consumes how many time. The Xdebug debugger already contains a profiler. Profiling shows you the bottlenecks in overview
- mod_gzip which is available as an Apache module compresses your data on the fly and can reduce the data to transfer up to 80%
- Excellent Article about optimizing php by John Lim
Credit: http://reinholdweber.com/
Friday, October 26, 2007
Setup tftp server on Ubuntu/Kubuntu
$sudo apt-get install xinetd tftpd tftp
2. vim /etc/xinetd.d/tftp and put this entry:
service tftp
{
protocol = udp
port = 69
socket_type = dgram
wait = yes
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd
server_args = -s /tftpboot
disable = no
}
3. Make /tftpboot directory
$ sudo mkdir /tftpboot
$ sudo chmod -R 777 /tftpboot
$ sudo chown -R nobody /tftpboot
4. Start tftpd through xinetd
$ sudo /etc/init.d/xinetd start
5. Testing. Transfer file rex.rex from 10.10.1.1 (Client using tftp) to
192.168.1.100 (Server 10.10.1.1):
root@BIKOL:/# touch rex.rex
root@BIKOL:/# chmod 777 rex.rex
root@BIKOL:/# tftp 10.10.1.1
tftp> put test.txt
tftp> quit
root@BIKOL:/# ls /tftpboot/ -l
total 0
-rw------- 1 nobody nogroup 0 2007-10-26 13:45 rex.rex
Credits: http://www.davidsudjiman.info/?p=93
Wednesday, October 24, 2007
Basic Syslog Configuration on Linux/Ubuntu
a look on this page
(http://www.linuxhomenetworking.com/wiki/index.php/Quick_HOWTO_:_Ch05_:_Troubleshooting_Linux_with_syslog)
whenever my syslog is not working (ie when something is broken,
misconfigured, etc). Thats when I was learning the Fortigate device, and
testing/tuning some IPS signatures.
Tuesday, October 23, 2007
Ubuntu 7.10 (Gutsy Gibbon)
That's right! Yesterday, I was brave enough to do the upgrade. Just clicked the update notification icon to install some (security) updates. When the update was done, the Upgrade notification flashed, ready to install.
It took some hours to finish the Ubuntu upgrade. Then, the VMware Workstation needed to be re-setup (as always) because some vmware modules need to be recompiled according to your running kernel version.
Note: To check your current kernel version, type uname -r at the console.
Whenever you need to install/re-install VMware on Linux, always remember the vmware-any-any* patch because you'll most likely need it for recompiling some vmware's components, like vmmon, etc.
And whenever you need it, just look for the updated version because its also being modified regularly. Thanks to the readily available solution to my problem:
http://ubuntu-tutorials.com/2007/09/26/how-to-install-vmware-server-on-ubuntu-710/
As I've said, its worth it for the wait ;-)
Monday, October 22, 2007
Where to go in Canada?
Here's some info that could help you:
Canada's best places to live
Friday, October 19, 2007
Sunday, October 07, 2007
Virus infection through web surfing
So if you're the bad ass hacker, where do you want to implant those malicious scripts/codes that would lead to virus infection? Good candidates would be those popular sites such as social networking sites (friendster, myspace, etc), or the likes of youtube, digg, and other very popular sites. Then that guy would do his trick to persuade you on clicking his malicious link (unless hes got new technique (i mean, new vulnerability probably, or any way to exploit some security loopholes) how to download and execute his program to user's pc automagically =)).
Take a look on this example of an entry on digg:
 Its "Eva Longoria sex tape" That would be very tempting to check out isn't it? =P Now, the bad ass will post a comment specifying the link for the video. And because you're excited to see it (who wouldn't?), you clicked the link and the browser will of course drive you to the destination.
Its "Eva Longoria sex tape" That would be very tempting to check out isn't it? =P Now, the bad ass will post a comment specifying the link for the video. And because you're excited to see it (who wouldn't?), you clicked the link and the browser will of course drive you to the destination.But the website (supposedly hosting the sex video) displayed some (fake) error message and would want you to install something to correct the error. Needless to say that the program it offered you to download and install is most likely a malicious software. Its usually a small program that when run, would download another (malicious) program, and the infection proceeds.
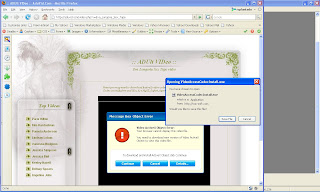
Because of some security measures from web browsers, automatic download and execute are now commonly prevented. Bad hacker must find a way (some sort of new vulnerability) to do the automatic download and execute from web browser. Otherwise, all they can do is to trick the user to download and run their code. In other words, don't run any program from untrusted source!
If your antivirus software didnt catch it, just send it to online virus scanners like virustotal or virusscan. Some AV products might have already detection for it:
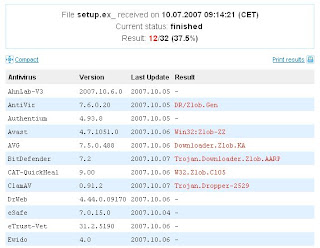
If you're curious what the f$%k is it doing, check their website for virus description. If no analysis for it yet, send it to sunbelt's malware analyzer. Thanks to sunbelt for its wonderful free service that would save some precious time analyzing some malware. In fact, I've sent the sample to sunbelt and the complete analysis can be found here.

Unless you have free time to dissect it by your own for curiosity, you can check my previous post on tools that could help you reverse engineer a malware.
Clearly, when you check the sunbelt's analysis for its activities, it's a malicious program that downloads another programs (could be another virus or worms) from a remote websites, executes it to the PC, modifies some registries to run everytime , drop other components and so on so forth - typical malware behavior.


